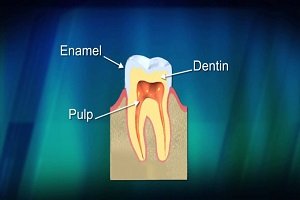
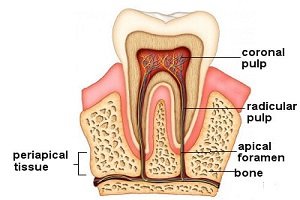
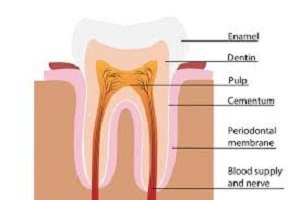
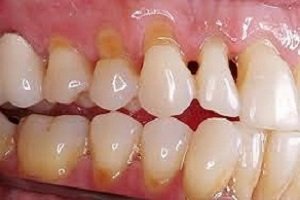
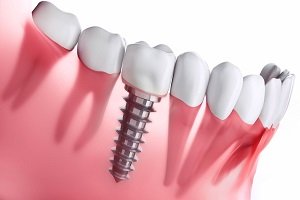
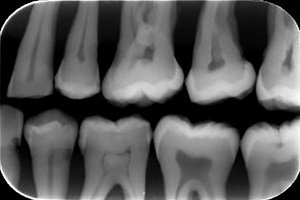
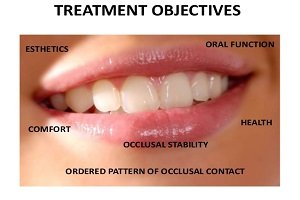
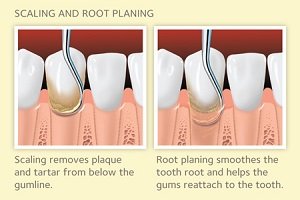
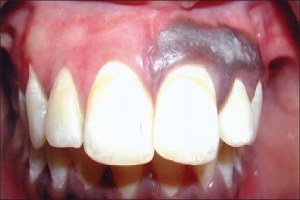
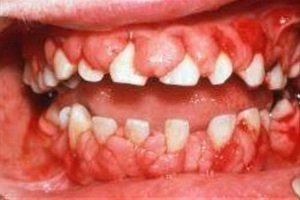
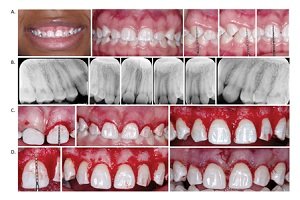
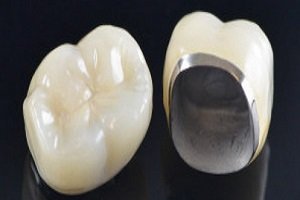
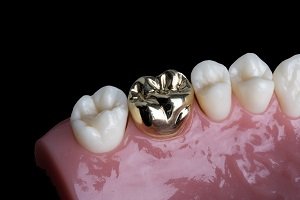
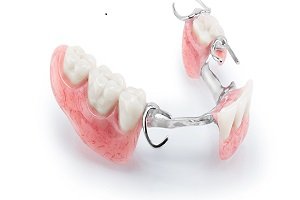
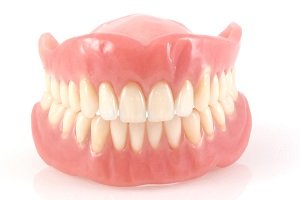
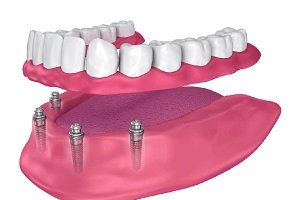
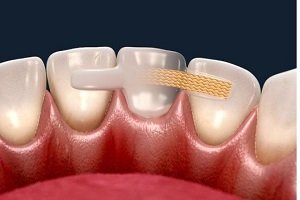
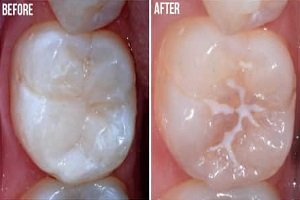
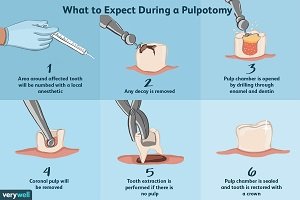
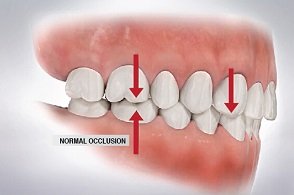
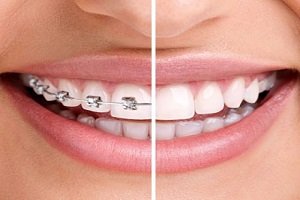
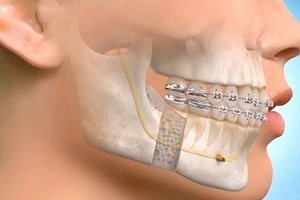
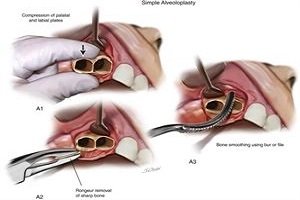
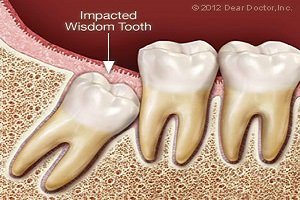
Enamel
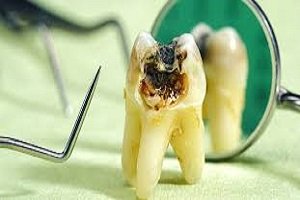
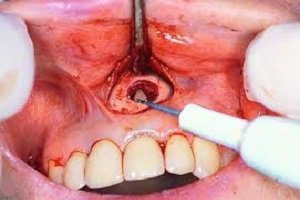
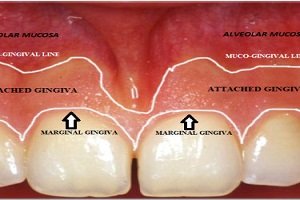
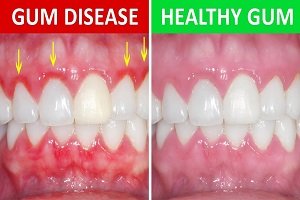
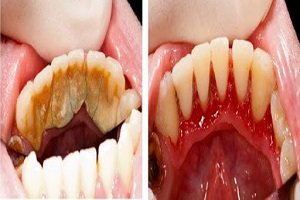
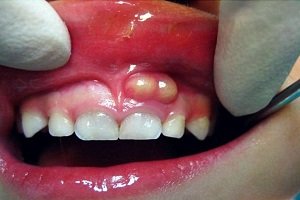
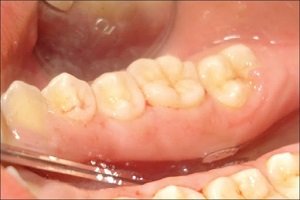
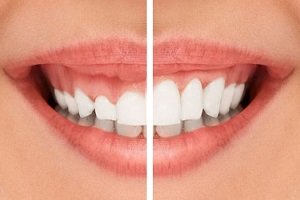
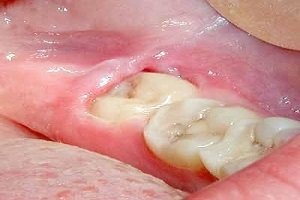
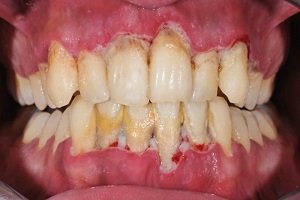
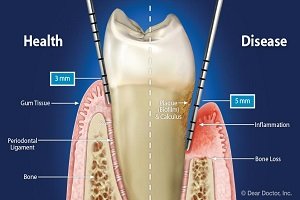
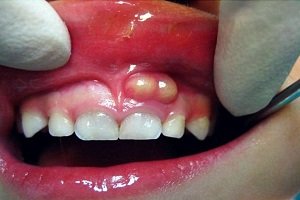
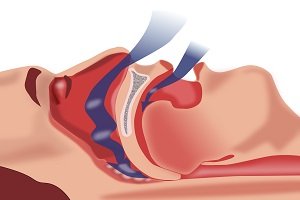
Enamel is the thin outer most covering of the tooth. This tough shell is the hardest tissue in the human body. Enamel covers the crown which is the part of the tooth that is visible outside of the gums. Because enamel is translucent, you can see light through it.